Ovarian and Uterine Tumors in Cows

Various abnormalities and pathological changes can occur in the reproductive system of cows. They affect the animal’s overall health, fertility, and the course of the estrous cycle—among others, through disturbances in prostaglandin secretion and, consequently, the lack of luteolysis of the corpus luteum.
These changes may have a hormonal background or result from mechanical injuries.
Cervical Abscesses
One of the causes of their development may be damage to the cervix during insemination procedures, uterine flushing, or embryo transfer–related procedures. It should also be remembered that the cervix may be injured during calving, especially if it is not adequately dilated. After implementing appropriate antibiotic therapy and successful treatment, there is a chance of effective fertilization in subsequent estrous cycles.
Pathological Changes Involving the Ovarian Bursa
This group includes, among others:
• adenomas,
• adenocarcinomas,
• hyperplasia of the ovarian bursa.
Ovarian Granulosa Cell Tumor
Most often detected during a per rectum examination, usually only once it has reached a considerable size and causes noticeable deformation of the ovary.
PEComa
A newly described mesenchymal tumor of the ovary, identified in cows suffering from adenomyosis or endometriosis.
Other Neoplasms of the Reproductive System
• leiomyomas,
• fibromas,
• sarcomas.
In my practice, I most frequently encounter postpartum abscesses of the uterine wall. In cases where the tumor does not infiltrate the uterine lumen, proper estrus preparation and insemination often result in success. However, it should be remembered that uterine stretching caused by the growing fetus may lead to abscess rupture, damage to the uterine wall, hemorrhage, or the development of inflammatory conditions.
The situation is significantly worse when the tumor penetrates the uterine lumen. In such cases, without intensive antibiotic therapy (often combined—systemic and local) and hormone therapy, the effectiveness of insemination is minimal.
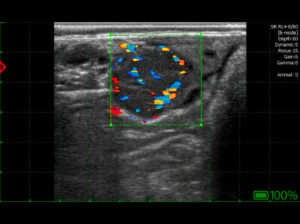
Doppler ultrasound examination may be helpful in diagnostics and prognosis assessment. The presence of blood flow within the lesion increases the likelihood of successful systemic antibiotic therapy, as the drug is able to reach the site of infection.

DVM, Michał Barczykowski